What Is a Good Random Read Speed
When it comes to SSD vs. HDD speed comparisons, SSDs clearly has the advantage. However, historically the higher price per Gigabyte of SSD storage meant that the benefits of higher SSD speeds were restricted to a few applications where the cost could be justified.
Today, though, the price differential has narrowed significantly. And with the significantly college SSD speeds in contrast to HDD, the popularity of SSD storage, often known as '"flash," is exploding. Businesses are now focused on getting the best flash array.
In the marketplace for the best SSDs? Encounter our list of the all-time and fastest SSDs.
SSD vs. HDD Speed and Performance
Solid state drives (SSDs) are faster than conventional hard disk drives (HDDs) and they are likewise more reliable and utilise less power. That ways that when information technology comes to choosing between SSD or HDD storage, SSDs would exist preferably to HDDs in all cases if it weren't for one fact: SSDs are more expensive than HDDs when measured past cost per Gigabyte of storage.
To understand why at that place is a large divergence between SSD v HDD speed, it's necessary to consider the divergence between SSD and HDD technology.
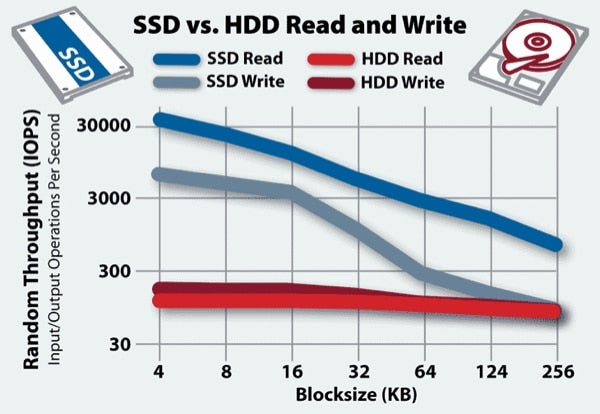
Solid state drives have dramatically faster read and write speeds when compared with hard disk drives.
How does Hard Drive Speed Work?
An HDD is made up of a number of spinning magnetic platters that stores data, and a number of read/write heads on mechanical arms that motility over the surface of the platters. To read or write data at a specific sector of a platter, the head has to move to the appropriate position, so wait for the sector to laissez passer underneath it as the platter rotates.
This fashion of operation presents two obvious sources of delay:
- Information technology takes time for the head to move to the right position, known equally seek time.
- There is a filibuster as the head waits for the right role of the platter to come up around, known as rotational latency, or simply latency.
The seek time depends on where the head is at the start of an operation and where it has to move to, and the latency depends on the position of the deejay in its bicycle, then for a given HDD it is normal to talk nigh boilerplate seek time and boilerplate latency.
One more potential source of delay is the HDD interface through which data on the drives is transmitted to a connected estimator or storage system. Only common interfaces such as SATA and SAS have been designed with hard bulldoze performance in mind, and these tend non to be a limiting factor to HDD read and write speeds.
When it comes to hard drive speed measurements, there are iv that are of import:
- Sequential read speed, reading from a big block of face-to-face data.
- Sequential write speed, the same, but for writing information.
- Random read speed, reading data scattered all over the disk.
- Random write speed. Random speeds are generally far lower than sequential speeds because of the amount of seeking and rotational latency involved.
How does SSD Speed Work?
The way that an SSD bulldoze works is completely different than a HDD. It uses a solid state storage medium, typically NAND (often known equally flash), and information is written to or read from the NAND by a controller, which effectively is the brains of the device.
With an SSD there is no variable seek time or rotational latency, as every part of the SSD tin be accessed in the same amount of time. But SSD read and write speeds are asymmetric: data reads are very rapid, but SSD write speeds are somewhat slower.
That's considering SSD storage is made up of individual NAND cells which can store one (or just a few) bits of information, and groups of cells are organized into pages. Finally, groups of pages are organized into blocks.
The problem is that data cannot exist written to a cell unless information technology is first erased, removing whatever existing information, and while data tin can be written one page at a time, it can but be erased in entire blocks at a time. That ways that to write a unmarried bit of data to a cell information technology is necessary to copy all the pages in the cake containing that cell to a holding area, erase the entire block, and then write all the pages and the new scrap of data back to the erased block.
Is an SSD Faster than an HDD?
The simple answer to this question is yes, and the reason is that the solid-state nature of SSD storage gives it a huge speed reward over the mechanical design of HDD storage, with the inherent delays that information technology entails.
SSD vs. HDD Read/Write Speed
How much faster is an SSD? The answer of course depends on which SSD and HDD yous compare and what exactly you are comparing. An SSD speed comparison will reveal that there is a wide variation between SSD speeds.
But to go an idea of the operation difference an SSD v HDD speed comparison could reasonably evidence, a standard SSD can read sequential data at a speed of nigh 550 megabytes per second (MBps) and write it at 520 MBps. In dissimilarity, a fast HDD may comport out sequential reads and writes at just 125MBps.
That shows that the deviation between SSD and HDD performance is significant. The respond to the question of how much faster an SSD is compared to an HDD? Most four times faster when it comes to SSD vs. HDD read speed, and a little less when SSD vs. HDD write speed is compared.
SSD Read/Write Speed
Historically, SSDs take been designed to be drop-in replacements for HDDs, and that ways that they are frequently made with the same interfaces as HDDs, which in practice ways a SATA interface, or on more loftier-performance systems, a SAS interface.
These interfaces have been optimized specifically for HDD storage devices, but they are suboptimal for SSDs. "Interfaces do make it the way for SSDs," says Jim Handy, an annotator at Objective Analysis, "and that's why we are seeing PCIe SSDs."
The effect of size on speed: SSD Interfaces
To go an thought of the benefit of a more than SSD-friendly interface like PCIe, consider this. The SATA 3.0 specification simply allows SSDs to reach a maximum data rate of most 560MB/due south. By dissimilarity the PCIe 3.0 interface allows speeds of 985MB/s per lane. (The SSD's controller is connected past multiple lanes to dissimilar NAND chips where the data is actually stored.) Even though an individual NAND chip is unlikely to exist able to piece of work at a 985MB/s, a device with 8 chips on separate lanes can easily offer 3000 MB/s amass throughput.
How to brand SSDs faster
Another mode that SSD speed can be increased is to use faster NAND. Standard NAND used in SSDs is effectively flat, and performance-sapping error correction algorithms are used to mitigate against data abuse caused by jail cell to cell interference in closely packed cells. But new flash scrap technology uses multiple layers of memory cells (known as 3D NAND) and this offers the potential for faster SSD read and write performance. That's because it's not necessary to run these algorithms in 3D NAND, and chip-maker Samsung says its 3D NAND is twice equally fast as conventional planar NAND when it comes to SSD write speed.
The departure between SSD and HDD read speeds can be enhanced further past moving away from NAND birthday, and instead using SSDs which are equipped with a new storage medium called 3D XPoint, jointly developed by Intel and Micron.
Hard Bulldoze Read/Write Speed
The biggest delays that limit HDD speed are seek times (the delay every bit the read/write head moves into position) and latency (equally the hard bulldoze waits for the required function of the deejay to rotate into position under the head), as explained earlier.
Then it follows that by reducing these two factors, the divergence between SSD and HDD performance can exist narrowed.
How to make HDD speed faster
The way to reduce latency is relatively unproblematic: increasing the rotation rate of the platters volition reduce latency, and for that reason high-performance HDDs rotate at xv,000 rpm rather than the more standard vii,200 rpm.
Rotating the platters faster than 15,000 would result in further reductions in latency, but for practical reasons this is difficult to achieve: the faster the platters spin the less stable they are. Faster spinning disks also consume far more power. Both of these issues have been addressed in part by filling HDDs with helium , just for the moment 15,000 rpm appears to exist the limit.
Short Stroking
Reducing seek times to increase HDD performance is possible, and this is unremarkably accomplished using a trick called "short stroking". This involves using but a portion of an HDD'southward capacity, for example by only using the outermost ten% of each platter. By doing this, the read/write head only has to encompass a distance 1 tenth as far every bit if the whole platter was in use, and on average information technology will be far closer to where it needs to motion to for each read or write functioning.
The downside to short stroking is that although there will exist a significant increase in difficult drive speed, it is extremely inefficient because only a small portion of the HDD storage chapters tin can be utilized even though the power consumption remains unchanged.
Instance Speed Comparison of SSD vs. HDD
Information technology's difficult to get an exact "ssd to hdd" speed comparison, because other factors like interface also play a role. Merely permit's wait at two mainstream devices to get a rough comparison.
SSD speed comparisons are complicated by the fact that dissimilar devices with unlike interfaces and storage technologies bear very differently. However, to go an idea of the current state of SSD technology, this is the type of performance available today on a very fast SSD, along with a fast HDD.
| Speed Comparison | |
|---|---|
| HDD read/write speed | UltraStar DC HC620 with SAS 12GB/s interface Sustained transfer rate: 255 MBps read and write |
| SDD read/write speed | Samsung 970 Evo with PCIe 3 interface Read speed 3,500 MBps max. Write speed ii,500 MBps max. |
Boot Speed
Since whatever SSD vs. HDD speed comparing will bear witness that SSDs offering superior performance, it is not surprising that there is a growing trend towards placing operating systems on SSDs. As well every bit resulting in a general performance hike, this also results in a system boot speed, which is much quicker than the aforementioned organization booting an operating system stored on an HDD.
How much quicker? The precise increment in boot speed using an SSD vs an HDD will depend on a variety of factors, only in general it is not unreasonable to expect an comeback of 200% – 800%.
To put that into context, a Windows system with an SDD could be expected to boot up in about 20 seconds, while the same system with an HDD could easily take betwixt xl seconds and a minute and half to boot up. In function the divergence may exist accounted for by the fact that an HDD takes time to spin up to its operating speed when powered on, only the difference is mainly accounted for by the much faster read speeds that an SSD can offering during the read-intensive kicking process.
Criterion
SSDs and HDDs are commonly supplied with manufacturers' specifications, but to get the best SSD v HDD speed comparison between two specific devices y'all need to run an SSD vs. HDD performance benchmark exercise using benchmarking software.
This software is designed to measure transfer speeds under different conditions such as sequential reads and writes (where all the data is in the same surface area), and random reads and writes (to different parts of the storage medium).
Popular SSD vs. HDD performance benchmark software includes:
CrystalDiskMark: This is a popular and like shooting fish in a barrel-to-use tool which carries out both SSD and HDD benchmarking.
Atto Disk Benchmark: This is a widely-accepted tool that tin can criterion SSDs and HHD, likewise every bit RAID arrays and host connexion to fastened storage.
Source: https://www.enterprisestorageforum.com/hardware/ssd-vs-hdd-speed/
0 Response to "What Is a Good Random Read Speed"
Post a Comment